Teenage Benzodiazepine Abuse: A Parent’s Guide
Benzodiazepines are medications often prescribed for anxiety or sleep disorders. However, they carry a risk of addiction, especially among teenagers.
This article will shed light on benzodiazepine addiction, focusing on how it affects adolescents. As parents, your child’s health and future are paramount, and being informed is the first step to help them.
Key Takeaways
Benzodiazepines, often referred to as “benzos,” are medications used for anxiety, sleep disorders, and other conditions, but they carry a risk of addiction, especially in teenagers.
- Benzodiazepines enhance the calming effects of the neurotransmitter GABA in the central nervous system.
- Common uses of benzodiazepines include treating anxiety, sleep disorders, seizure disorders, and muscle relaxation.
- Side effects of benzodiazepines can be both physical and psychological, with the risk of dependence and overdose.
- Parents should understand the risks associated with benzodiazepines and ensure safe use by adhering to prescription guidelines and proper storage.
Remember that you’re never alone in your journey to support your teenager’s well-being. Call us at (845) 539-0834 for more information.
Understanding Benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines, often called “benzos,” are medications used to treat anxiety, sleep issues, and certain medical conditions. They work by calming the brain and nerves. Short-acting benzodiazepines are some of the most commonly prescribed medications. While helpful when used as prescribed, these drugs can become addictive if misused. This can happen to anyone, including teenagers.
Teenagers might first take benzos to cope with stress and later use them recreationally. The risk of addiction increases in teens because their brains are still developing.
If you suspect your teen is struggling with benzodiazepine addiction, seek professional help. Treatment options are available to support their recovery journey. Understanding benzos and their potential risks is the first step in helping your teen make healthier choices.
How Benzodiazepines Work
Understanding how Benzodiazepines work in the body is essential to grasp their potential risks and impact on the central nervous system.
Impacting the Central Nervous System: Benzodiazepines affect the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Benzos boost the effects of a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GABA’s role is to calm the nervous system, like a soothing massage to the brain.
Interaction with GABA Receptors: Benzos interact with GABA receptors in the brain, making them more responsive to GABA. This enhanced response slows down nerve impulses in the brain, leading to a calming effect. This can be beneficial for those dealing with anxiety. However, long-term use of benzodiazepines can cause tolerance, where a person needs more of the drug to achieve the same effect. This can result in adverse effects and increase the risk of addiction.
Be aware of the potential for benzodiazepine addiction and withdrawal symptoms when using these drugs, especially if not taken as prescribed. Combining benzodiazepines with alcohol can have dangerous effects on the nervous system. Use these medications under the guidance of a medical professional.
Uses of Benzodiazepines
Let’s explore the common uses of benzodiazepines.
Side Effects of Benzodiazepines
The side effects of benzodiazepines can be both physical and psychological.
Physical Side Effects
Following are some of the most common physical side effects:
- Drowsiness: Benzodiazepines can make a person feel extremely tired, sometimes to the point of nodding off during the day.
- Dizziness: Teens may experience unsteadiness or vertigo when using these medications.
- Memory Problems: Some teens may have trouble remembering things or feel mentally foggy.
- Nausea and Vomiting: The drug use can sometimes upset the stomach and lead to vomiting.
- Slurred Speech: Speech may become unclear or slurred while using benzodiazepines.
- Impaired Coordination: Teens may struggle with tasks requiring coordination, such as driving.
- Respiratory Depression: In high doses or when mixed with other substances like alcohol or opioids, benzodiazepines can slow down breathing, which can be dangerous.
Psychological Side Effects
Here are the psychological side effects:
- Mood Changes: Benzodiazepines can lead to mood swings, making teens more irritable or anxious.
- Confusion: Some teenagers may become confused or disoriented while on these medications.
- Aggression: In rare cases, benzodiazepines can trigger aggressive behavior.
- Dependence: Teens can develop a physical and psychological dependence on benzodiazepines, leading to cravings and strong withdrawal symptoms when not using them.
- Increased Risk of Sexual Assault: Misusing benzodiazepines can increase teenagers’ risk of sexual assault.
- Risk of Overdose: Combining benzodiazepines with other substances like opioids can enhance the risk of overdose, which can be life-threatening.
Parents should discuss the potential side effects of benzodiazepines with their child’s healthcare provider and closely monitor their teenager’s use of these medicines. Being informed and vigilant can help protect your teen’s well-being and safety.
Risks Associated with Benzodiazepine Use
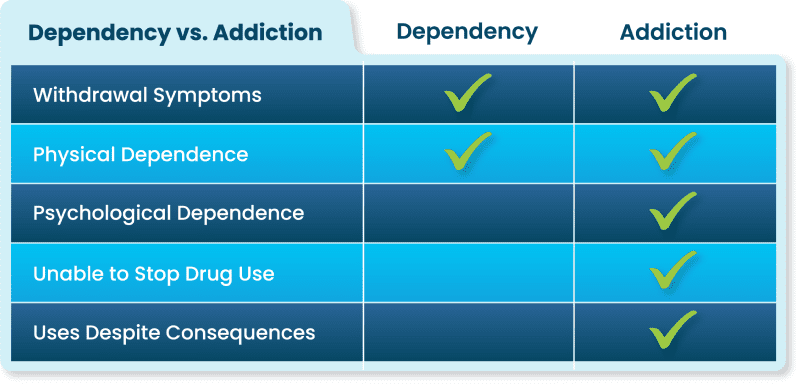
For parents concerned about their teenagers’ well-being, understanding the risks of benzodiazepine use is crucial, especially in the context of teenage addiction. Two significant risks associated with these medications are dependency and overdose.
Dependency and Addiction: Benzodiazepines, prescribed for conditions like anxiety and insomnia, can cause dependency and addiction, even when used as directed by healthcare professionals. Teens may rely on these medications to cope with stress or anxiety, which can develop into a more profound physical dependence.
Withdrawal symptoms can be intense when they try to stop, often leading to continued use. The longer a teenager uses benzodiazepines, the higher the risk of addiction, making it crucial for parents to be vigilant about their teen’s medication use. Talk to your child’s doctor if you suspect they are becoming dependent on the drug and discuss other options for care.
Overdose: Combining benzodiazepines with other substances like alcohol, opioids, or illegal drugs can lead to a dangerous overdose. This combination can depress the central nervous system, causing slowed breathing and loss of consciousness, which can be life-threatening. Overdose risk is especially high when teens use benzodiazepines that aren’t prescribed or take larger doses than recommended.
Being informed about the risks of dependency and overdose associated with benzodiazepine use is essential for parents. Open communication with healthcare professionals and discussing these concerns with your teenager can help prevent potential harm.
Benzodiazepine Withdrawal
Parents and teenagers need to understand the potential challenges of withdrawal. Here, we’ll outline the symptoms of benzodiazepine withdrawal and how to manage them.
Symptoms of Benzodiazepine Withdrawal
Benzodiazepine withdrawal can be uncomfortable and challenging, especially for teenagers who have become dependent on these medications. Here are some common withdrawal symptoms:
- Anxiety and panic attacks
- Restlessness and irritability
- Insomnia or trouble sleeping
- Muscle tension and pain
- Tremors or shaking
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sweating and increased heart rate
- Difficulty concentrating
- Sensory sensitivities (e.g., light or sound sensitivity)
- Hallucinations or perceptual disturbances
In summary, understanding and addressing these symptoms with healthcare professionals’ guidance is crucial for effective management and recovery.
Benzodiazepine Withdrawal Management
Teen addiction treatment specialists can create a plan to manage benzodiazepine withdrawal. This plan often includes the following:
- Medical Supervision: Withdrawal can be challenging, and medical professionals can provide the necessary support and monitoring to ensure the teen’s safety.
- Tapering: Gradually reducing the dose of benzodiazepines is often recommended to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
- Psychological Support: Counseling and therapy can help teens cope with anxiety and other emotional challenges during withdrawal.
- Alternative Therapies: Non-addictive medications or cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can manage anxiety and panic disorder.
- Support System: A strong support system, including family and friends, is crucial for teenagers during withdrawal.
Parents need to seek help from healthcare professionals specializing in addiction treatment when their teenager struggles with benzodiazepine withdrawal. With guidance and support, teens can overcome addiction and work towards a healthier, drug-free life.
Safe Use of Benzodiazepines
For parents concerned about their teenager’s well-being and the potential for addiction, ensure the safe usage of benzodiazepines in your home. Here, we’ll discuss prescription guidelines and understanding dosages.
Prescription Guidelines
Benzodiazepines should only be used when prescribed by a healthcare professional. Parents should ensure that their teenager takes these medications exactly as directed. Communicate openly with the healthcare provider about any concerns or changes in the teenager’s condition. Be aware of the following prescription guidelines:
- Dose: The doctor will assess the right dosage based on the teenager’s specific needs and the type of benzodiazepine prescribed.
- Duration: Benzodiazepines are typically prescribed for short-term use to avoid the risk of dependence. Long-term use should only occur under close medical supervision.
- Monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider can help assess the effectiveness of the medication and any potential side effects.
Understanding Dosages
Understanding the prescribed dosage is essential to ensure safe usage. Parents should:
- Read Labels: Carefully read the medication label and any information the pharmacist provides.
- Ask Questions: If there are any doubts or concerns about the dosage, don’t hesitate to ask the healthcare provider or pharmacist for clarification.
- No Sharing: Benzodiazepines should never be shared with others, as they may have different needs and risks.
- Proper Storage: Keep the medication in its original container, out of reach of others, and follow any storage instructions.
Ensuring safe usage of benzodiazepines is vital in preventing teenage drug abuse and addiction. Open communication with healthcare professionals and adherence to prescribed guidelines can help protect your teenager’s well-being.
Get Help
If you’re suffering from benzo addiction, getting help as early as possible is essential. Benzo addiction is a severe illness that can lead to many problems. Getting help as early as possible can significantly improve your chances of recovery. Call us to get started with treatment.
Our resources are available to help you overcome your addiction with evidence-based therapies and innovative treatments proven by medical science to effectively manage your addiction. Our admissions counselors can help you learn more about the disease and how to keep it out of your life. Contact us confidentially today.
Secure Your Teen’s Future with Personalized Care
Are you worried about your teenager’s well-being in the face of benzodiazepine abuse? It’s time to take action and ensure their safety.
We provide expert guidance, counseling, and support tailored to your child’s needs. Don’t wait for addiction to take hold. Contact our team today for the knowledge, resources, and assistance you need. Call us at (845) 539-0834 for more information.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is an example of a benzodiazepine?
One common example of a benzodiazepine is diazepam, known by its brand name Valium. Diazepam is prescribed to treat anxiety, muscle spasms, and seizures. It belongs to a class of medications that affect the central nervous system to provide relaxation and relief from these conditions. It’s essential to use benzodiazepines only as a healthcare professional prescribes to minimize the risk of dependence and misuse.
What conditions is benzodiazepine usually used to treat?
Benzodiazepines are typically prescribed to treat anxiety disorders, panic disorder, insomnia, muscle spasms, and certain seizure disorders. They are medications that can provide short-term relief from these symptoms. Still, they should be used under the direction of a healthcare professional due to their potential for dependence and misuse.
What are the side effects of benzodiazepines?
Side effects of benzodiazepines can include drowsiness, dizziness, memory problems, nausea, slurred speech, impaired coordination, and, in higher doses, respiratory depression. Psychological side effects may include mood changes, confusion, aggression, and dependence. Misusing benzodiazepines can also increase the risk of overdose and sexual assault.