Addiction is a complex and pervasive phenomenon that touches the lives of millions worldwide, transcending social, cultural, and economic boundaries. It’s a compelling force that binds individuals to substances or behaviors, often against their will, wreaking havoc on their physical, mental, and emotional well-being.
This intricate web of dependence is shrouded in misconceptions, stigmas, and myths. From the brain’s delicate chemistry to the diverse range of substances and behaviors that can trap us, understanding addiction is the first step towards compassion, support, and, ultimately, breaking free from its formidable grip.
Continue reading to unravel the enigma of addiction and discover the profound insights that can pave the way for recovery and healing.
Key Takeaways
Addiction can affect anyone, whether it’s through the misuse of prescription medications or illegal drugs. Here’s what you need to know:
- Addiction is a complex brain disorder characterized by compulsive substance use or behavior despite adverse consequences.
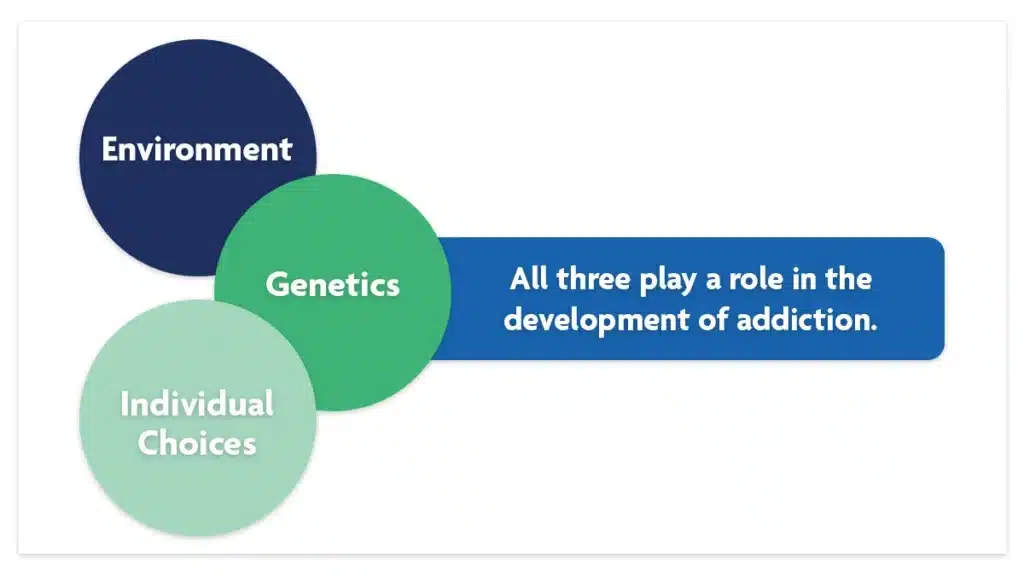
- Genetics, environment, and individual choices all play a role in the development of addiction.
- Therapy, medication, and support systems can help young adults recover and live healthier lives.
Contact our teen treatment center at (845) 479-6888 for more information on drug recovery treatment services to embrace a healthier and happier life.
What is Addiction?
Addiction is a complex and chronic condition characterized by the compulsive use of a substance or engagement in behavior despite its harmful consequences. It is often associated with substances like illicit drugs or alcohol, but addiction can also manifest in activities like gambling, gaming, or even shopping.
It is marked by an inability to control one’s impulses, leading to negative physical, psychological, and social consequences.
Science Behind Addiction
Addiction is rooted in changes that occur in the brain over time. Repeated exposure to a substance or behavior triggers the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. This reinforces the desire to continue the addictive behavior.
Neuroadaptations in the brain can make quitting difficult and contribute to withdrawal symptoms when the substance or behavior is removed.
The Brain’s Role in Addiction
The brain’s reward system, including the nucleus accumbens, prefrontal cortex, and amygdala, plays a critical role in addiction. The nucleus accumbens processes feelings of pleasure, while the prefrontal cortex is involved in decision-making and impulse control.
Over time, drug use can disrupt the balance between these brain regions, leading to impulsive, compulsive behaviors.
Chemical Imbalances and Addiction
Addiction often leads to chemical imbalances in the brain. The brain may produce less dopamine naturally, leading to feelings of depression and anxiety when not engaging in the addictive behavior.
This further reinforces the cycle of addiction, as individuals turn to the substance or activity to alleviate these negative feelings.
Age and Addiction
Addiction can affect individuals of any age, from adolescents to older people. Teenagers are particularly vulnerable to addiction due to the ongoing development of their brains. The prefrontal cortex, responsible for impulse control and decision-making, is not fully developed until the mid-20s.
This makes adolescents more prone to impulsive behavior and risk-taking, increasing the likelihood of experimenting with addictive substances or behaviors.
Signs of Addiction
Signs of addiction can vary depending on the substance or behavior involved, but common indicators may include:
Physical Signs
- Dilated or constricted pupils
- Frequent tremors or shakes
- Sudden weight loss or gain
- Poor hygiene and appearance
- Track marks or needle punctures
Psychological Signs
- Strong cravings for the substance or behavior
- Increased anxiety, depression, or mood swings
- Difficulty focusing or concentrating
- Denial of the addiction
- Obsession with obtaining the substance
Behavioral Signs
- Neglecting responsibilities or obligation
- Isolating from friends and family
- Engaging in risky behaviors to obtain the substance
- Failed attempts to cut back or quit
- Lying or secretive behavior related to the addiction
If you recognize these signs and symptoms in your family member, seek immediate help from a healthcare provider.
Myths About Addiction
There are many myths and misconceptions about addiction, which can contribute to stigma and misunderstanding. Addressing these myths can help to make a more informed and compassionate approach to mental illness.
Here are some common myths about addiction:
Myth 1: Addiction is a Choice
Myths about addiction persist, often fueling misconceptions and stigmatization. Myth 1 claims addiction is a choice, but it’s a complex interplay of genetics, environment, and brain chemistry. No one willingly chooses addiction.
Myth 2: Only Certain Types of People Develop Addiction
Myth 2 perpetuates the belief that only certain people become addicted. In reality, addiction knows no boundaries, affecting individuals of all backgrounds, races, and socioeconomic statuses. It doesn’t discriminate.
Myth 3: You Can Stop Addiction on Your Own
Myth 3 suggests one can conquer addiction solo, but recovery is often a challenging journey requiring support and professional help. Overcoming substance use disorder (SUD) often necessitates a multifaceted approach, including therapy, medication, and a strong support system.
Impact of Addiction On Health
Addiction exerts a profound toll on individuals’ health, with physical, mental, and emotional consequences. Substance abuse can lead to various health issues, including cardiovascular problems, respiratory diseases, liver damage, and an increased risk of infectious diseases like HIV.
Moreover, addiction often co-occurs with mental health disorders, exacerbating symptoms and impairing overall well-being. For example, depression and anxiety are common comorbidities with addiction, creating a complex web of challenges.
Economic Cost of Addiction
The economic burden of addiction is substantial. It encompasses healthcare costs, lost productivity, and criminal justice system expenses. Healthcare expenses arise from treating addiction-related ailments and managing the collateral damage they cause.
According to reports, lost productivity results from absenteeism and reduced workplace efficiency. Additionally, addiction to illicit or prescription drugs fuels criminal activity, further straining resources and public finances.
Social Impact of Addiction
Addiction fractures families and communities, fostering alienation and social instability. Families often bear emotional and financial burdens, leading to strained relationships and broken homes. Communities grapple with increased crime rates, strained social services, and diminished well-being.
Stigmatization of young adults struggling with addiction compounds these challenges, hindering their recovery and societal reintegration.
Addiction Treatment Approaches
Effective addiction treatment typically involves a combination of medical, psychological, and social interventions.
The following are some common components of addiction treatment:
Detox
Detoxification, or detox, is the crucial first step in substance use disorder treatment. It involves the removal of the addictive substance from the body, which can be a challenging process, accompanied by withdrawal symptoms.
Medical supervision is often necessary during detox to ensure the safety and comfort of the individual. Detox helps clear the path for further treatment by addressing the physical aspect of addiction.
Inpatient Treatment
Inpatient or residential treatment programs provide a structured and supportive environment for young people struggling with drug abuse. These programs offer 24/7 care and access to medical professionals, therapists, and support staff.
Inpatient treatment allows for a comprehensive approach to addiction, addressing both the physical and psychological aspects. It also provides a break from the environments and triggers that may contribute to addiction.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a widely used therapeutic approach in addiction treatment. It helps individuals identify and modify unhealthy thought patterns and behaviors associated with addiction.
By learning new coping skills and strategies, patients can develop healthier ways to deal with cravings and stressors, ultimately reducing the risk of relapse.
Dual Diagnosis Treatment
Many teens struggling with addiction also have co-occurring mental health disorders. Dual-diagnosis treatment addresses both addiction and mental health issues concurrently. Integrated care ensures individuals receive the necessary support and therapies to manage their conditions effectively.
Support Groups
Support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) and Narcotics Anonymous (NA) play a crucial role in addiction recovery. These groups offer a sense of community, shared experiences, and a platform to discuss challenges and successes openly. Peer support is a valuable resource for maintaining long-term sobriety.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the main points of addiction?
Addiction is characterized by compulsive engagement in a substance, including heroin, cocaine, marijuana, or behavior, despite adverse consequences. It involves tolerance (needing more for the same effect), withdrawal symptoms, loss of control, and a preoccupation with obtaining and using the addictive substance or engaging in the behavior.
How does addiction affect both physical and mental health?
Addiction can harm physical health by causing organ damage, increased chronic disease risk, and withdrawal symptoms. It impairs mental health through anxiety, depression, and altered brain function, disrupting daily life and relationships. Effective treatment and support are crucial for recovery.
What are some surprising facts about addiction recovery?
Surprising facts about addiction recovery include the potential for lifelong susceptibility to relapse, with some individuals remaining in recovery indefinitely. Support from peers and communities plays a vital role, and recovery often involves discovering new passions and purpose.
Many people successfully overcome drug addiction and lead fulfilling lives.
Drug and Alcohol Recovery for Teens
At our residential treatment program, we offer a nurturing environment designed to help adolescents break free from the grips of addiction, whether it’s alcohol, heroin, cocaine, or opioids.
Our dedicated and compassionate medical professionals combine evidence-based treatment, educational workshops, and recreational activities to create a comprehensive recovery plan.
Moreover, our art and music therapies assist young adults in breaking the addiction cycle and exploring creative outlets for long-term healing. Give your teen the chance they deserve. Contact us at (845) 479-6888 for more information.