As a parent or loved one, watching a teen struggle with addiction can feel overwhelming. But there’s a beacon of hope: cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). This approach offers practical help for your teen, guiding them toward recovery and healing.
By working closely with a trained therapist, teens learn practical strategies to cope with cravings, manage triggers, and build healthier habits. Read on to explore the transformative potential of CBT in combating substance addiction among teens.
Key Takeaways
Substance addiction is a serious issue among teens in the United States. However, there is hope: cognitive behavior therapy (CBT). This article covers:
- CBT helps teens identify and alter negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with addiction.
- The process of CBT for addiction follows a structured approach that often begins with assessment.
- Various techniques are employed in CBT, aimed at helping teens address different aspects of their addiction.
Contact our teen rehab facility today at (845) 479-6888 to learn how our inpatient program can help your child on their journey toward recovery.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) For Addiction
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), a form of talk therapy, is a widely used therapeutic approach for addressing addiction. It’s based on the idea that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected, and by changing our thoughts and behaviors, we can effectively change how we feel and manage addictive behaviors.
In CBT for addiction, individuals work with a therapist to:
- Identify Triggers: Recognize the situations, emotions, or thoughts that trigger cravings or substance use.
- Develop Coping Skills: Learn and practice coping skills to manage cravings, urges, and stressful situations without resorting to substance use.
- Challenge Distorted Thinking: Explore and challenge negative or irrational thoughts and beliefs about oneself, others, and the world that may contribute to addictive behavior.
- Behavioral Experiments: Engage in behavioral experiments to test the validity of negative beliefs and develop more adaptive ways of thinking and behaving.
- Relapse Prevention: Develop strategies to prevent relapse and maintain sobriety, including identifying early warning signs and creating a plan for handling high-risk situations.
CBT for addiction is typically short-term and goal-oriented, with a focus on practical strategies that individuals can apply in their daily lives. It can be delivered in individual or group therapy sessions and may be integrated with other approaches such as medication management, family therapy, or support groups.
Overall, CBT is considered one of the most effective treatment options for substance use disorder (SUD), with research supporting its efficacy across a range of substances, including alcohol, opioids, cocaine, and cannabis.
The Process Of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for drug and alcohol addiction in teens typically follows a structured process. Here’s a general overview of the process.
Assessment
The process begins with a thorough assessment by a trained therapist. This assessment assists in identifying the underlying factors contributing to the teen’s addiction, such as past trauma, family dynamics, or co-occurring mental health disorders.
Setting Goals
Once the assessment is complete, the therapist and teen collaboratively set goals for therapy. These goals provide a roadmap for the treatment process, outlining what the teen hopes to achieve and how they plan to get there.
Psychoeducation
Psychoeducation is a vital component of CBT for addiction. Teens learn about the effects of drugs and alcoholic drinks on the brain and body, as well as the cycle of addiction. Understanding these concepts empowers teenagers to make informed decisions about their recovery.
Identifying Cognitive Distortions
CBT helps teens identify and challenge cognitive distortions—negative thought patterns that contribute to addictive behaviors. By recognizing and disputing these distortions, teens can begin to change their thinking and break free from the cycle of addiction.
Thought Restructuring
Thought restructuring involves replacing negative thoughts with more balanced and realistic ones. Teens learn to question the validity of their automatic thoughts and develop healthier ways of thinking about themselves and their circumstances.
Homework Assignments
CBT often involves homework assignments to reinforce the skills learned in therapy sessions. These assignments may involve practicing coping strategies, keeping a journal of thoughts and feelings, or engaging in activities that promote sobriety.
Monitoring Progress
Throughout the therapy process, the therapist monitors the teen’s progress and adjusts treatment strategies as needed. This might involve revisiting goals, refining coping skills, or addressing new challenges that arise.
Termination and Relapse Prevention
As therapy nears completion, the focus shifts to termination and relapse prevention. Teens learn strategies for maintaining sobriety in the face of triggers and cravings, as well as how to create a support network to help them stay on track.
Remember, CBT is just one component of a comprehensive treatment approach. Depending on the teen’s needs, additional interventions may be incorporated into the treatment plan.
Techniques Used In Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for addiction in teens typically involves a variety of techniques aimed at addressing different aspects of addiction.
Functional Analysis
This technique helps teens understand the triggers and consequences of their drug and alcohol abuse. By identifying the thoughts, feelings, and situations that lead to drug use, teens can learn healthier ways to cope with challenges.
Behavioral Activation
Behavioral activation encourages teens to engage in positive activities that bring them joy and fulfillment. By replacing substance use with enjoyable and meaningful activities, teens can reduce their reliance on drugs.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Mindfulness practices teach teens to stay present in the moment and manage cravings without judgment. Relaxation techniques, such as progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) and deep breathing, help teens reduce stress and anxiety, making it easier to resist the urge to use drugs.
Stress Management Skills
CBT equips teens with practical skills to manage stress effectively. This may include problem-solving techniques, time management strategies, and healthy coping mechanisms to deal with daily life’s challenges without resorting to substance abuse.
Exposure Therapy
Exposure therapy helps teens confront their fears and cravings in a safe environment. By gradually exposing themselves to triggers without using drugs, teens can build resilience and confidence in their ability to resist temptation.
Motivational Enhancement
Motivational enhancement techniques help teens explore their reasons for change and strengthen their commitment to recovery. By identifying personal motivations, teens become more determined to overcome drug use disorders.
Contingency Management
Contingency management involves rewarding positive behaviors, such as staying sober or attending therapy sessions, with incentives. This reinforces healthy habits and encourages teens to stay on track with their recovery goals.
Social Skills Training
Social skills training helps teens develop healthy relationships and communication skills. Building a supportive network of peers and loved ones enhances their ability to resist peer pressure and maintain sobriety.
By integrating these techniques into therapy sessions, therapists can help teens develop the necessary skills and strategies to overcome drug and alcohol use disorder (AUD).
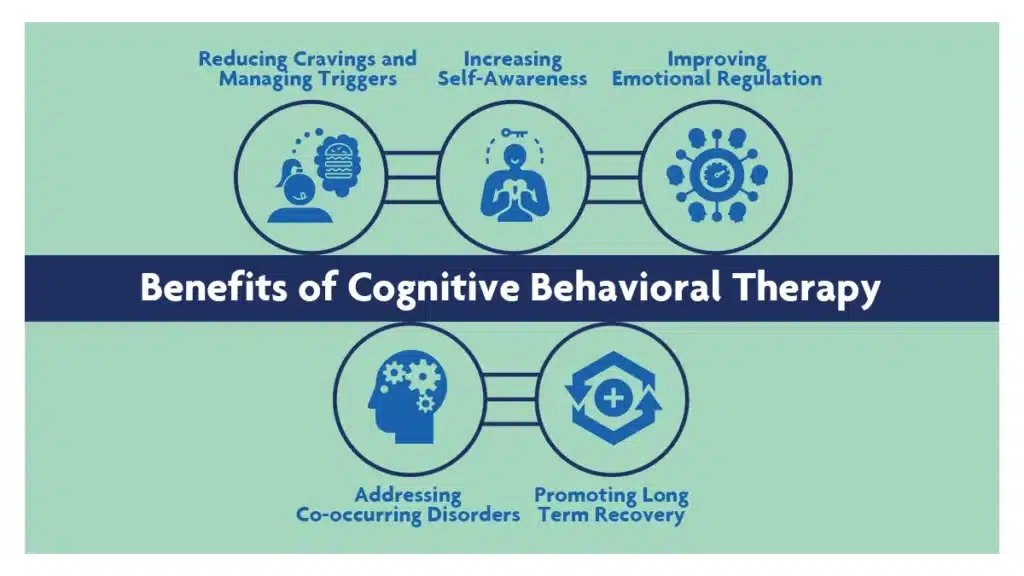
Benefits Of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) offers valuable tools for teens struggling with substance abuse and addiction. Here’s how this form of therapy can help.
Reducing Cravings and Managing Triggers
CBT equips teens with strategies to cope with cravings and navigate triggers without resorting to substance use. By identifying triggers and developing coping skills, teens gain greater control over their urges and reduce the risk of relapse.
Increasing Self-Awareness
Through CBT, teens gain insight into the thoughts, emotions, and behaviors driving their addiction. By increasing self-awareness, teens become better equipped to recognize and challenge negative patterns, paving the way for positive change.
Improving Emotional Regulation
CBT teaches teens to identify and regulate their emotions effectively. By learning healthy coping mechanisms, they can manage stress, anxiety, and other triggers without resorting to substance use as a means of escape.
Addressing Co-occurring Disorders
Many teens struggling with addiction also experience co-occurring mental disorders such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). CBT addresses these underlying disorders alongside addiction, providing integrated treatment to address the complex needs of teens.
Promoting Long-Term Recovery
CBT focuses on building the skills and resilience needed for long-term recovery. By empowering teens to make positive changes in their thoughts and behaviors, CBT lays the foundation for a sustainable and fulfilling life free from addiction.
Supporting Family Involvement
CBT recognizes the importance of family support in the recovery process. Therapists work collaboratively with family members to provide education, guidance, and support, fostering a supportive environment for teen recovery.
In short, CBT offers hope and healing for teens struggling with addiction, empowering them to build a brighter future free from substance abuse.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the cognitive approach to addiction?
The cognitive approach to addiction examines how thoughts influence addictive behaviors. It focuses on understanding the role of negative thinking patterns in fueling substance abuse. By addressing these thoughts, individuals can learn to change their behaviors and overcome addiction.
This approach helps people develop healthier coping strategies and gain control over their impulses. Through therapy, individuals can identify triggers, challenge distorted beliefs, and develop skills to resist cravings. Overall, the cognitive approach offers practical tools for managing addiction and achieving long-term recovery.
Is cognitive behavioral therapy effective for treating various problems such as depression, phobias, and addiction?
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a powerful tool in treating various problems like depression, phobias, and drug addiction. It helps individuals recognize and change negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with these issues.
By teaching practical skills to cope with challenges and manage symptoms, CBT empowers people to overcome their struggles and improve their mental health. Research has shown that CBT is a highly successful approach for addressing various psychological and behavioral problems.
What is the role of CBT in addiction treatment?
CBT plays a significant role in addiction treatment by helping individuals identify and alter negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with their substance use. Through CBT, individuals learn practical strategies to cope with cravings, manage triggers, and build healthier habits.
By addressing the underlying cognitive factors driving addiction, CBT empowers individuals to overcome drug abuse and achieve lasting recovery. It offers an organized and evidence-based approach to treatment, offering hope and practical solutions for those struggling with addiction.
Empowering Teens Toward Healing
Are you noticing changes in your teen’s behavior that could indicate struggles with drugs or alcohol? Don’t wait until it’s too late. Seeking professional help early can make all the difference.
Our teen treatment facility offers a residential treatment program designed to provide comprehensive support and care for your child. Our program includes individual counseling, group therapy, family therapy, educational workshops, and fun recreational activities like art and music therapy.
Take action today and give your teen the chance to thrive. Contact us at (845) 479-6888 to learn more about how we can help your family heal together.


